How does a smart scale work? How does it calculate the BMR, muscle mass, fat mass, etc.?
Discover how smart scales work and their role in weight loss. Learn about bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), body composition metrics like muscle mass and fat percentage, and how they calculate your Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR). This guide offers insights into utilizing smart scale data for effective weight management.

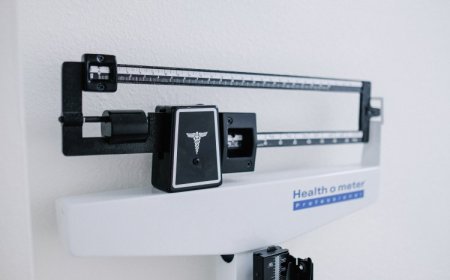
In the journey of weight loss and fitness, understanding your body composition is crucial. Smart scales have emerged as a popular tool, offering detailed insights beyond just your weight. Let's dive into how these innovative scales work and how they can aid in your weight loss journey.
Understanding Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
Smart scales employ a technique called bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA). When you step on these scales, a harmless electrical current zips through your body. This current travels differently through various tissues. For instance, it passes quickly through muscle (which is rich in water and electrolytes) and slower through fat. The scale measures the resistance or impedance this current faces, laying the groundwork for further analysis.
Calculating Body Composition
Using the resistance data, combined with personal details like your height and age, the scale's algorithms estimate your body composition. They can differentiate between your fat percentage and lean mass by understanding how the current was conducted through your body. These calculations are insightful but remember, they are best used to track changes over time rather than as absolute measurements.
Estimating Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Your BMR is the number of calories needed for basic functions at rest. Smart scales estimate this using formulas that consider your weight, height, age, and gender. Commonly used equations include the Harris-Benedict and Mifflin-St Jeor equations. While useful as a guideline, these are still estimates and can vary based on individual factors.
The Role in Weight Loss
For those on a weight loss journey, understanding and tracking changes in body composition can be empowering. Knowing the balance between fat and muscle mass helps tailor your diet and exercise plans. Moreover, understanding your BMR can guide your daily calorie intake decisions.
The Accuracy and Limitations
While smart scales are a convenient home tool, their accuracy can be influenced by hydration levels, recent exercise, and more. They are excellent for tracking trends but not for precise measurements. For more accuracy, methods like DEXA scans or hydrostatic weighing are preferable.
DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scans are a highly accurate and detailed method for assessing body composition. Initially developed to measure bone density, DEXA scans have become a popular tool for determining body fat percentage, lean muscle mass, and bone mineral content.
How DEXA Scans Work:
- Dual X-Ray Beams: DEXA uses two X-ray beams at different energy levels to scan the body. These beams pass through the body and are absorbed differently by bones, muscle, and fat.
- Separating Tissues: The scanner differentiates these tissues based on how they absorb each X-ray beam. This allows it to accurately measure the density of bone, the amount of lean muscle mass, and the volume of fat in the body.
- Whole-Body Scan: It usually involves a full-body scan that takes about 10 to 20 minutes. You lie still on a table while the scanner passes over your body.
Advantages:
- Accuracy: DEXA provides highly accurate and detailed measurements of body composition.
- Segmental Analysis: It can assess different body regions separately, which is beneficial for understanding muscle imbalances or regional fat distribution.
- Low Radiation: The amount of radiation exposure from a DEXA scan is very low, similar to natural background radiation experienced daily.
Limitations:
- Availability and Cost: DEXA scans are usually available in medical settings or specialized fitness centers and can be more expensive than other body composition methods.
- Radiation Exposure: Despite being low, it does involve exposure to radiation, which might not be suitable for everyone, especially pregnant women.
Hydrostatic Weighing
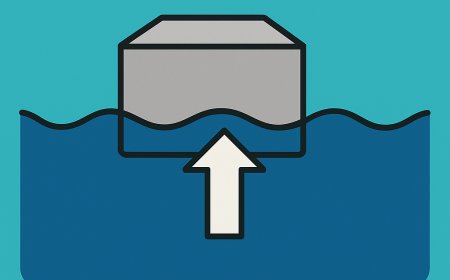
Hydrostatic Weighing, also known as underwater weighing or hydrodensitometry, is another highly accurate method for measuring body composition, particularly body fat percentage.
How Hydrostatic Weighing Works:
- Weighing Underwater: You are first weighed on dry land. Then, you are weighed again while fully submerged in a tank of water, after exhaling completely.
- Displacement Principle: The method is based on the principle of water displacement and Archimedes' principle. Muscle and bone are denser than water, whereas fat is less dense. The amount of water displaced by your body helps in determining your body density.
- Calculating Body Fat: From the body density, the percentage of body fat can be calculated using various formulas.
Advantages:
- High Accuracy: It's considered a gold standard for measuring body fat percentage.
- Scientifically Validated: The technique has a long history of use and extensive scientific validation.
Limitations:
- Accessibility and Comfort: Not widely available and requires special equipment. The process can be uncomfortable or impractical for some individuals (e.g., holding breath underwater).
- Skill Required: Accurate results depend on the skill of the technician and the subject's ability to fully exhale and remain still underwater.
Both DEXA scans and hydrostatic weighing offer precise measurements of body composition and are particularly useful in research, clinical settings, and for athletes who require detailed body composition analysis. However, for the general population seeking to track body composition changes, less invasive and more accessible methods like BIA smart scales might be more practical, despite their lower accuracy.
Conclusion
Smart scales offer a window into your body composition, playing a supportive role in your weight loss journey. While they provide valuable estimates, remember they are just one piece of the puzzle in your overall health and fitness approach.
What's Your Reaction?